Overview
The 3 Way Color Grade filter enables you to color correct an input image using industry standard Lift-Gamma-Gain controls with an intuitive color sphere and slider interface. The filter includes a built-in keying option for isolating secondary colors from the primaries and power window style masking (with 2 point motion tracking), which allow you to isolate or selectively apply the color correction to specific region of the image. Independent color correction adjustments can be applied to points inside and outside of the key-mask selection within a single instance of the filter.
Compare controls, located at the top of the filter, let you compare the input and processed image, or two independent color correction settings applied to the image. All internal processing in this filter is done in 32 bit floating point for maximum precision, thereby eliminating any round-off errors. This allows you to combine extreme settings of the different controls without introducing banding on the image output.
 3 Way Color Grade Control Overview
3 Way Color Grade Control Overview
Function
Presets and Common Controls
BCC filters come with a library of factory installed presets plus the ability to create your own custom presets and preview them with the BCC FX Browser™.
BCC filters also include common controls that configure global effect preferences and other host-specific effect settings.
For more information about working with presets and other common controls, Click Here.
Compare Mode
The BCC Compare Mode provides a convenient mechanism to compare the effect result with the original source layer. It provides several variations on basic split-screen views with the filtered clip placed next to the unedited original.
For more information on the Compare Mode,Click Here.
Compare Mode pop-up: Used to enable or disable the compare mode function.
- Off: The filtered output is displayed in the composite window, bypassing the compare mode controls.
- Side by Side: Splits the composite window in half along the horizontal axis. The output to each half is dependent on the selection in the Compare Type pop-‐up.
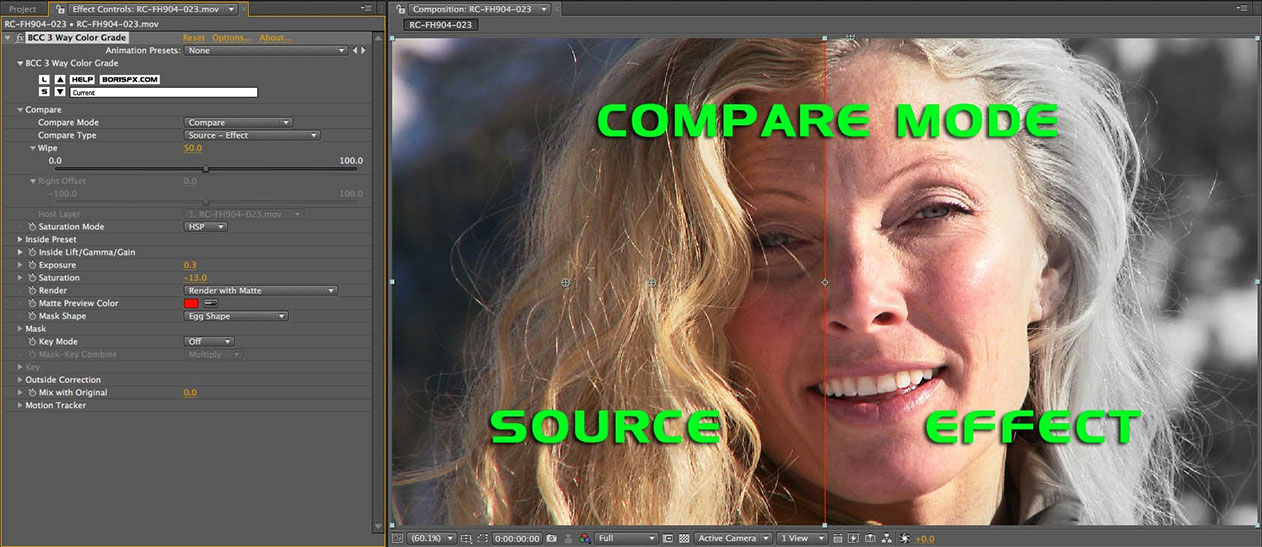
- Compare: Splits the composite window horizontally with a dragable wipe bar. The output to each half is dependent on the selection in the Compare Type pop-‐ up.
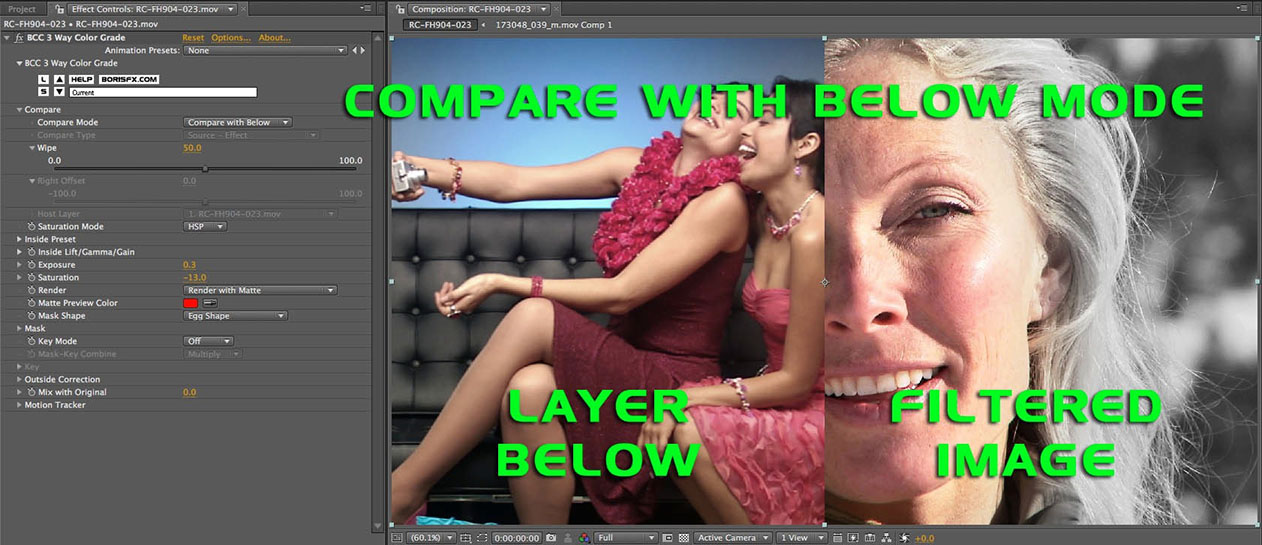
- Compare with Below: Splits the composite window horizontally with a dragable wipe bar. The layer below the filtered layer is displayed to the left of the wipe bar; the filtered layer is on the right.
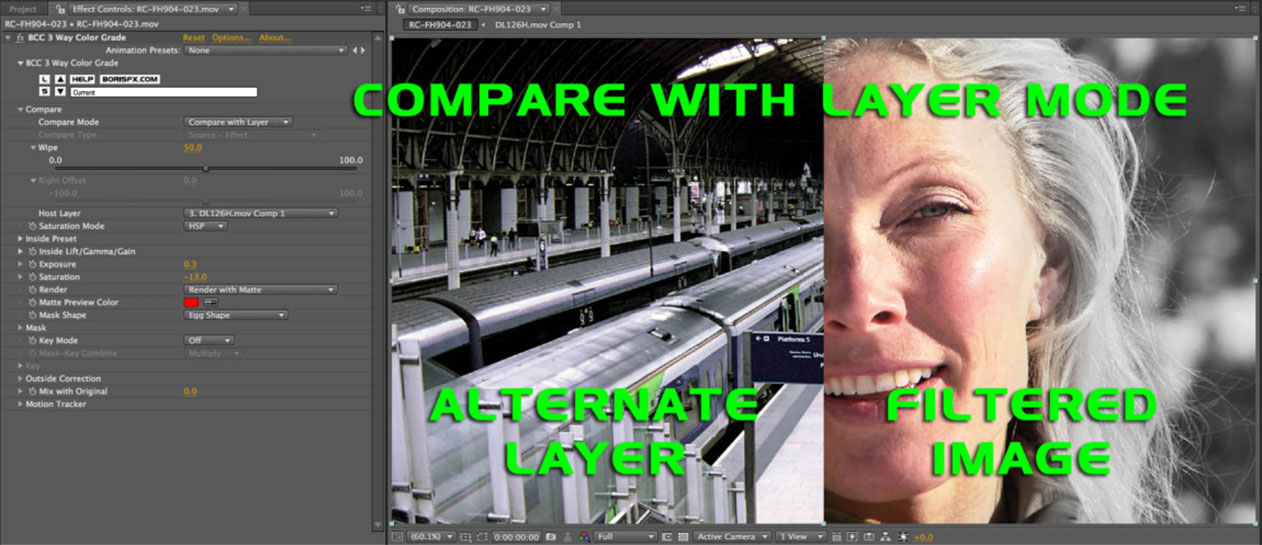
- Compare with Layer: Splits the composite window horizontally with a dragable wipe bar. A user-‐selected layer from the timeline is displayed to the left of the wipe bar; the filtered layer is on the right.
Compare Type: Used to control the output to the composite window when in side by side mode and includes the following options.
- Source - Effect: The unfiltered source input is on the left; the filtered source is on the right.
- Inside - Outside Correction: The result of the inside color correction set-‐up is on the left; the result of the outside color correction set-‐up is on the right.
Wipe parameter: Used to reposition the wipe bar in the composite window.
Right Offset parameter: Used to offset the image on the right side of the split screen.
Host Layer pop-up: Used to select the layer that is displayed when in compare with layer mode.
Compare Mode Usage Examples:
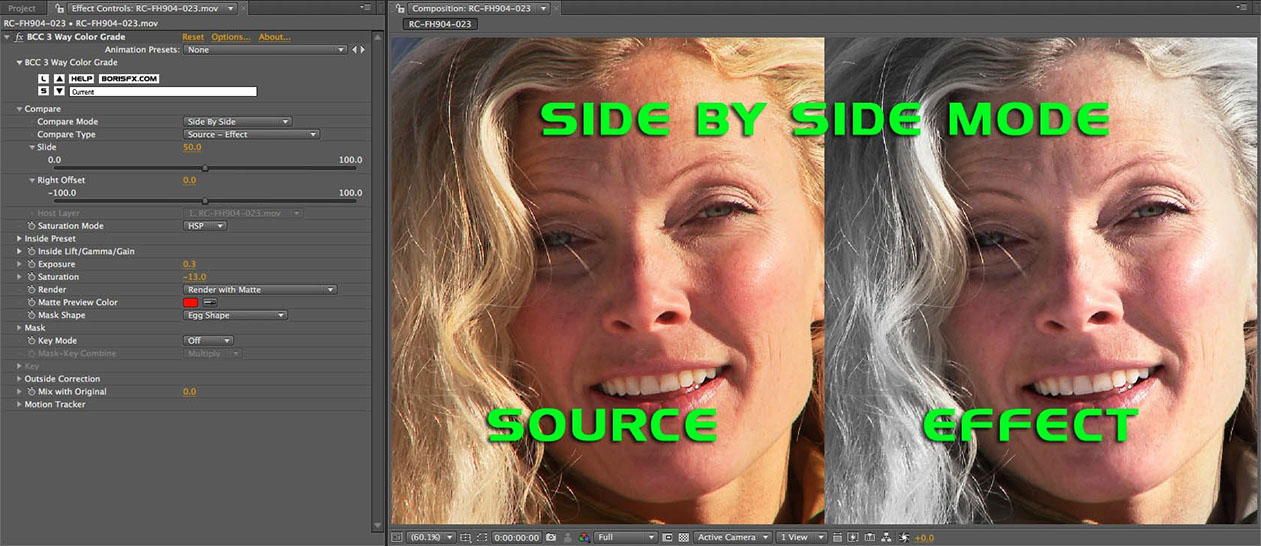 Side by Side Mode – Source Effect
Side by Side Mode – Source Effect
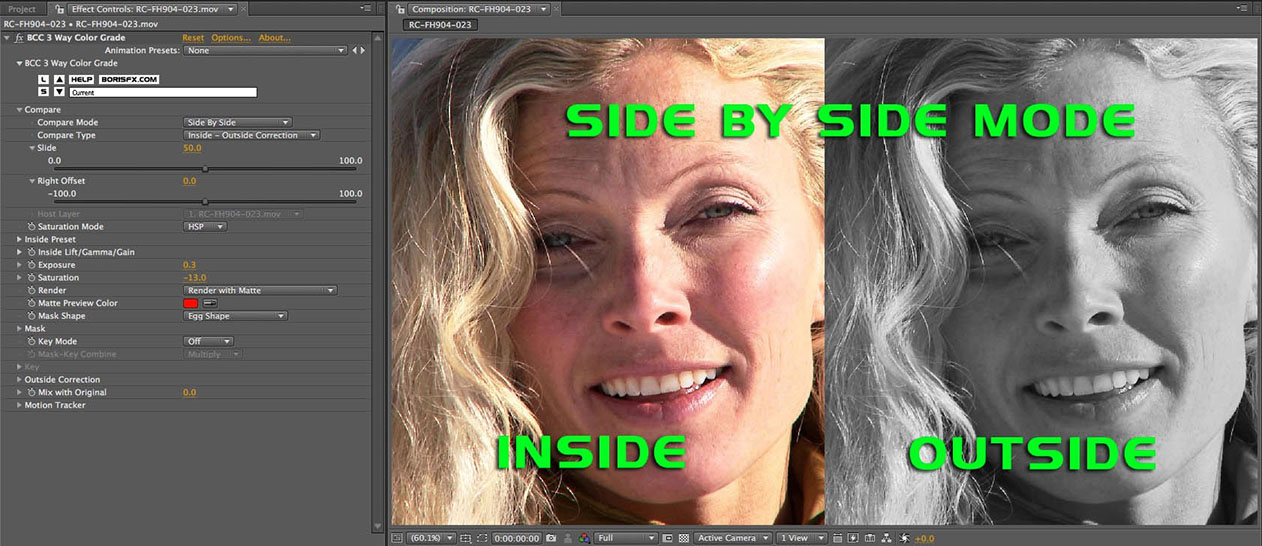 Side by Side Mode – Inside Outside
Side by Side Mode – Inside Outside
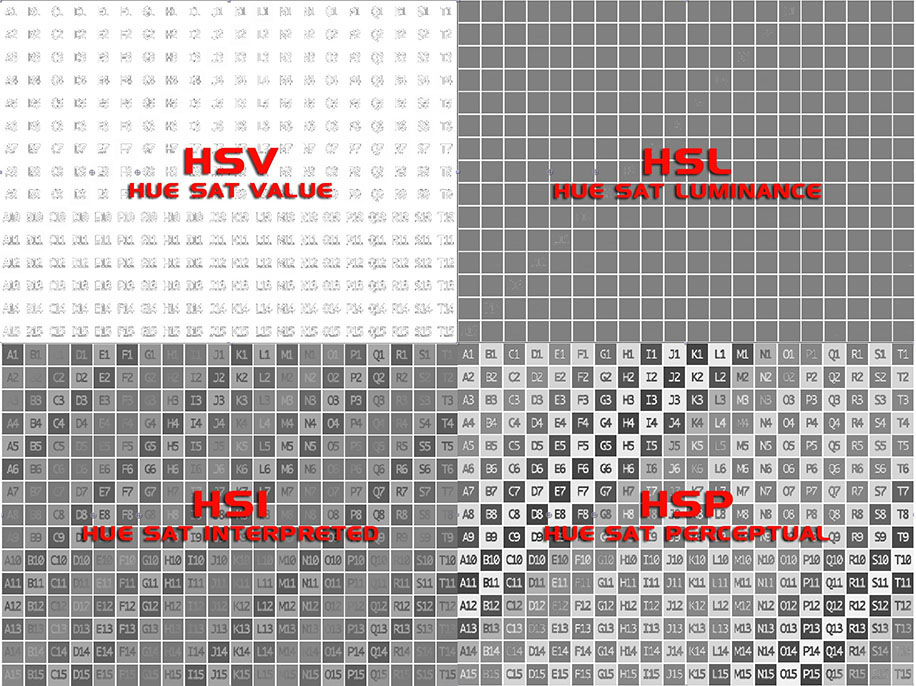
Saturation Mode: Used to set the color space or gamut in which the filter will perform changes to the saturation of the input clip, instructing the filter to process particular luma values in one of several separate ways when increasing or decreasing the Saturation of the input.
- HSV: Hue, Saturation, Value
- HSL: Hue, Saturation, Lightness
- HSI: Hue, Saturation, Interpreted
- HSP: Hue, Saturation, Perceptual
- HSLuma: Hue, Saturation, Luminance
Hint: Setting the Saturation Mode to HSP provides the greatest tonal range when generating black and white images.
Saturation Mode Examples:
 Saturation Mode Example – Source
Saturation Mode Example – Source
 Saturation Mode Example – Results
Saturation Mode Example – Results
Inside Preset pop-up selector: Used to store and or retrieve color settings that affect the region inside the masked or keyed region of the input. The settings in this group affect the 3 Color Wheel values, as well as the Exposure and Saturation parameter values
Inside Lift/Gamma/Gain group
Contains animatable Lift/Gamma/Gain interactive color spheres and luma controls. Note that while each of the three groups to some degree affects the entire image, the Lift controls are best suited for tuning the dark areas of the image, the Gamma controls for the mid-‐tones, and the Gain controls for the light areas.
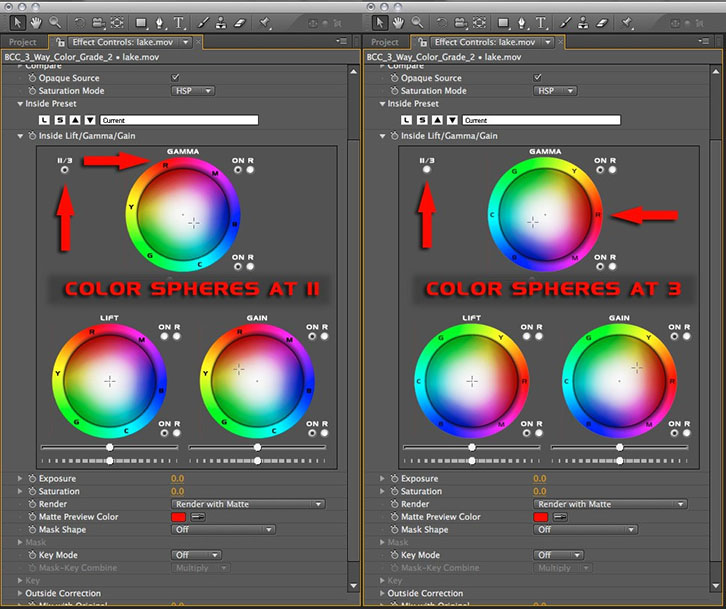
Located in the top left corner of the group is a switch labeled 11/3. This toggle switch enables you to change the origin or position of the color spheres to match that of a vector scope (where red is at approximately 11 o’clock) or that of a graphics application (where red is located at 3 o’clock).
Each color sphere has a control point that is used to adjust hue and saturation. The control point can be moved by interactively dragging it across the color sphere or by moving the cursor over the desired position on the sphere and clicking with the mouse / pen.
Beneath each color sphere is a pair of sliders that are used to adjust Luma values. The upper slider is used to make large adjustments to luma values, while the lower (dashed) slider is used to fine-tune the amount of Luma adjustment.
To enable animation for the controls in this group, click on the stopwatch function beside the group name. Once a keyframe has been added, you can add another by moving the CTI to another location on the timeline and changing any ball or slider setting.
Each of the color control spheres and the luma control sliders has an on/off switch and a reset switch. The on/off switch behaves like a checkbox toggle control – the reset switch resets the color sphere or luma sliders to their default neutral position.
- Lift / Gamma / Gain Color Spheres – Used to adjust the hue and saturation values of the input clip.
- Lift / Gamma / Gain Luma Sliders – Used to adjust the luma values of the input clip.
- On Switches – Used to enable or disable the color (hue and saturation) or luma adjustment individually for Lift, Gamma and Gain.
- R Switches – Used to reset the color sphere or luma sliders individually for Lift, Gamma or Gain to the default neutral position.
The image below shows the color spheres in the filters user interface – as you can see, the position of the color spheres can be set to match that of a vector scope or that of a typical graphics / compositing application.
Exposure slider: Lightens or darkens the image by the number of f-‐stops set in the slider. You can use this control to globally lighten or darken an image. The internal floating point image processing allows you to do this without introducing banding in the image result.
Saturation slider: Allows you to boost or cut the saturation of the image, with positive values increasing the saturation of the image input and negative values decreasing the saturation. A value of -100 will produce a pure black and white result. The precise effect of the saturation adjustment is determined by the Saturation Mode pop-up setting.
Hint: Setting the Saturation Mode to HSP provides the greatest tonal range when generating black and white images.
Render mode pop-up: This popup interacts with the Mask and Key controls and determines the rendered output of the filter. The Mask and Key controls can be used to create a matte that separates the image into Inside and Outside pixels. The following options are available in this pop-up:
- Render with Matte: Uses the inside settings to render pixels inside the matte (pixels that are both inside the mask and keyed in), and the outside settings to render pixels that are outside the matte.
- Render Inside Matte Only: Uses the inside settings to render pixels inside the matte, and leaves pixels outside the matte unchanged.
- Render Outside Matte Only: Uses the outside settings to render pixels outside the matte, and leaves pixels inside the matte unchanged.
- Use Inside Correction: The matte is ignored, and the inside correction is applied to the entire image.
- Use Outside Correction: The matte is ignored, and the outside correction is applied to the entire image.
- View Matte: The Matte is rendered as a black and white image.
- Mask Inside Pixels: The source is rendered with a ruby mask over the pixels that are inside the matte.
- Mask Outside Pixels: The source is rendered with a ruby mask over the pixels that are outside the matte.
- Make Alpha from Matte: Makes an alpha channel from the matte. This is composited with the image’s original alpha channel.
- Make Alpha from Inverse Matte: Makes an alpha channel from the inverted matte. This is composited with the image’s original alpha channel.
- Show Source: Displays the unfiltered and unmasked original input clip.
Matte Preview Color picker: Used to set the color of the mask overlay
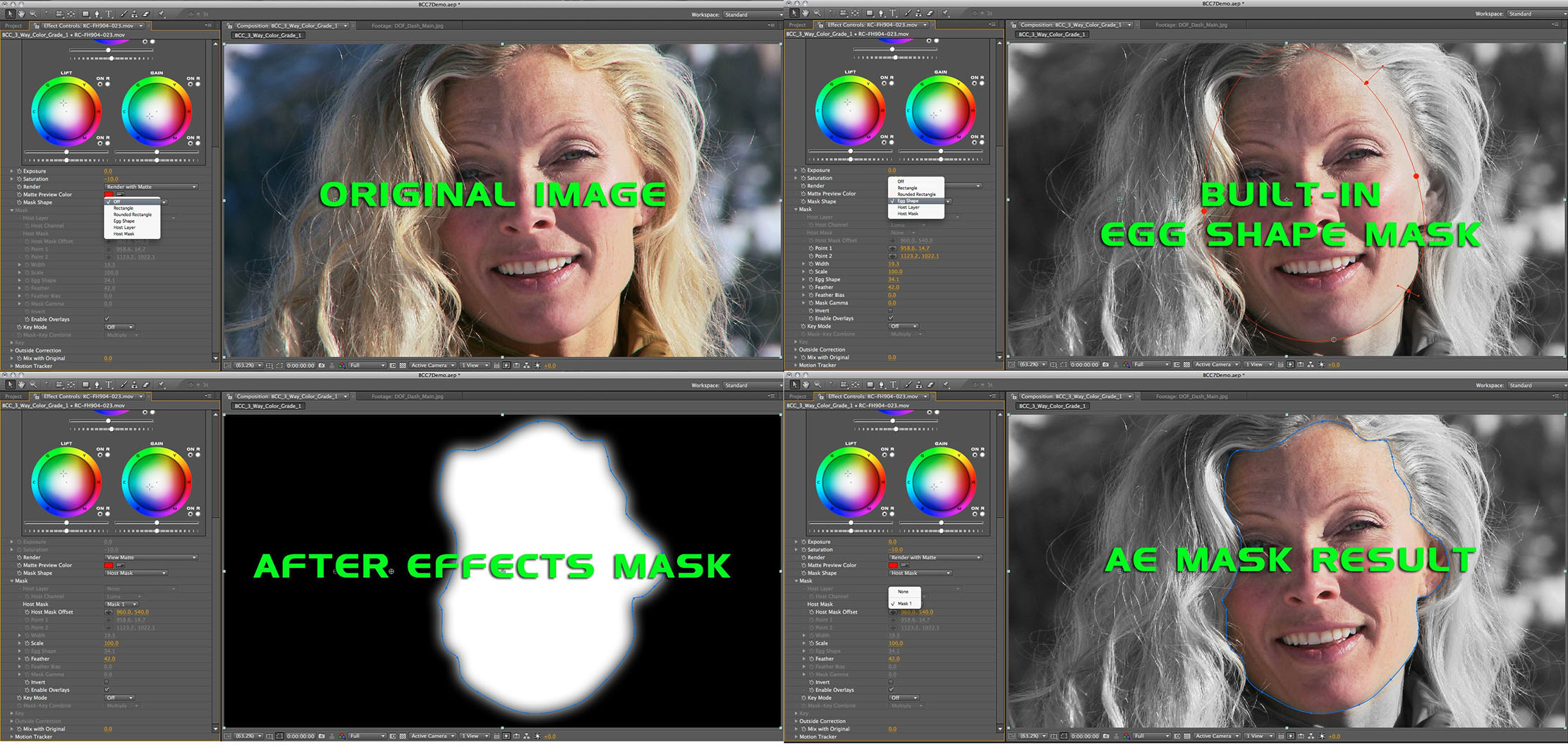
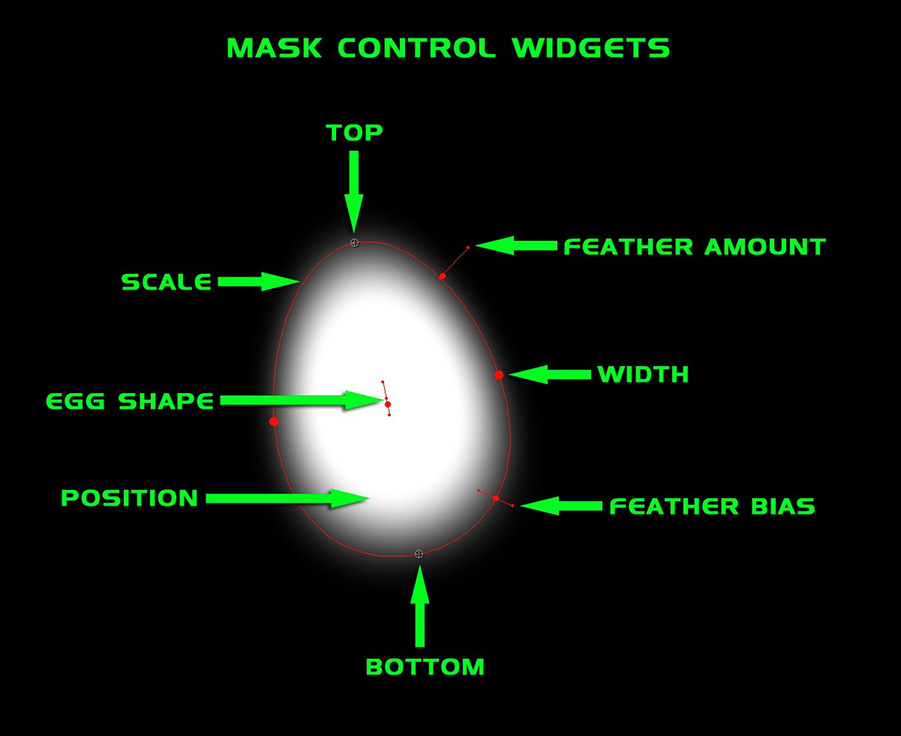
Mask Shape pop-up: Used to select the shape of the mask that is used to contain the inside and outside color correction. On-screen control widgets have been provided for the Rectangle, Rounded Rectangle and Egg Shape masks. The available on-screen controls for these mask shapes enable you to modify the position and scale of the mask as well as the feather amount, and feather bias. For the Egg Shape mask, an additional on-screen widget enables you to control the egg shape without taking your eyes off the image.
- Off: No mask is used and only the Inside Color Correction parameters will affect the image result.
- Rectangle: Generates a rectangular mask
- Rounded Rectangle: Generates a rectangular mask
- Egg Shape: Generates an egg shape mask (good for human faces)
- Host Layer: Uses luma values from the host layer
- Host Mask: Uses AE native mask shape
Note: If you select Host Layer or Host Mask, you must then proceed to the Mask Group to select a layer from the timeline or any single closed-‐spline AE mask shape. You will also need to go to the Mask group to modify any of the internally generated mask shape parameters.
 Mask Control Heads Up Display Widgets
Mask Control Heads Up Display Widgets
Mask Group
Contains parameters pertaining to the mask that is used to separate the inside and outside color grade.
Host Layer pop-up: Displays a list all of the available layers in the host timeline.
Host Channel pop-up: used to select the host layer luma or alpha channel or their inverts.
- Luma: Uses the selected host layer Luma channel.
- Alpha: Uses the selected host layer Alpha channel.
- Luma Inv: Uses the selected host layer Inverted Luma channel.
- Alpha Inv: Uses the selected host layer Inverted Alpha channel.
Host Mask pop-up: Displays a list of available host generated closed spline mask shapes.
Host Mask Offset: Used to offset the position of the selected host mask shape.
Point 1: Used to control the position of the top of the mask shape.
Point 2: Used to control the position of the bottom of the mask shape.
Width: Used to control the width of the mask shape.
Scale: Used to transform scale the mask shape.
Egg Shape: Used to control the mask egg shape. Negative values produce a downward pointing egg shape, positive values produce an upward pointing egg shape.
Feather: Used to control the softness (feather) of the mask edge.
Feather Bias: Used to position the feather inside or outside of the mask shape bounds.
Mask Gamma: Used to adjust the falloff of the mask feathering.
Invert: Used to invert the mask.
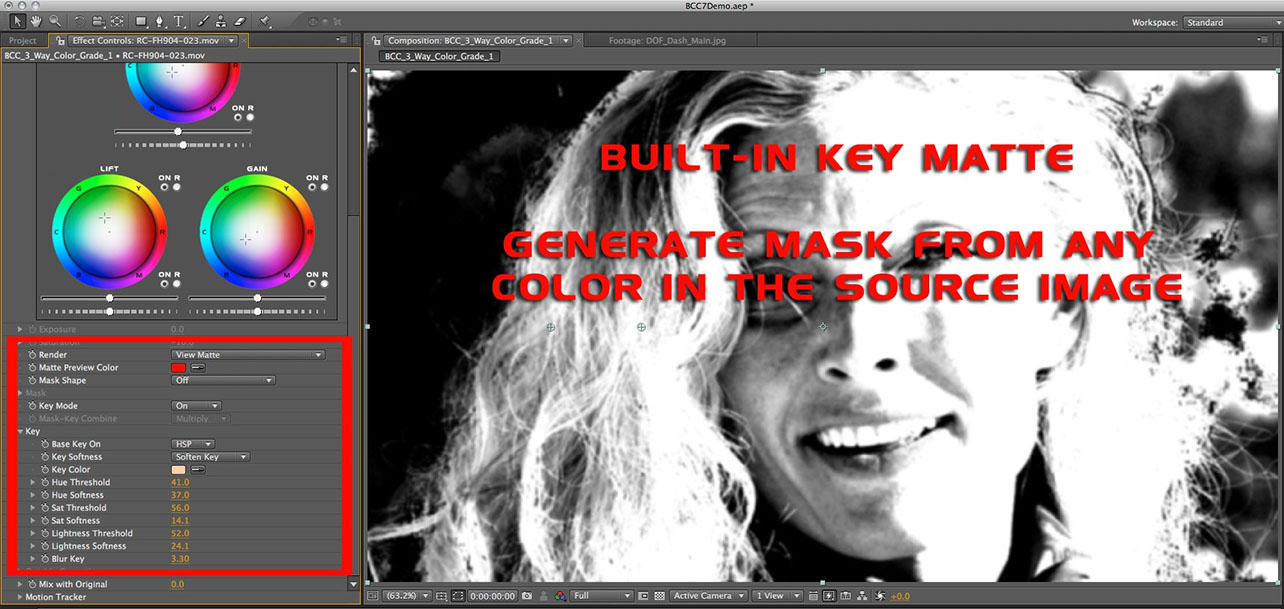
Key Mode pop-up: Controls the state of the key matte function.
Off: Key matte function is disabled.
On: Enables the key matte function.
Invert: inverts the generated key matte.
Mask Key Combine pop-up: contains options for combining the mask shape and the key matte.
- Multiply: Multiplies the key matte with the mask shape (removes pixels from the mask).
- Screen: Screens the key matte over the mask shape (adds pixels to the mask).
Key Group
Contains parameters that are used in the generation of key mattes to isolate secondary colors for color adjustment.
Base Key On pop-up: Used to set the color space in which the keying is done.
- HSV: Hue, Saturation, Luminance.
- HSL: Hue, Saturation, Value.
- HSI: Hue, Saturation, Interpreted.
- HSP: Hue, Saturation, Perceptual.
Hint: Setting the Base Key On pop-up to HSP provides the greatest tonal range of all the available options but it less bright than the HSL default.
Key Softness pop-up: Controls how the softness controls interact with the key.
- Expand Key: Increasing the softness controls expand the key when this is selected.
- Contract Key: Increasing the softness controls contract the key when this is selected
- Soften Key: Increasing the softness controls softens the key when this is selected.
Key Color swatch and eyedropper: Used to select a color from the image that will be matched in the selected color space.
- Note: If you choose a pure grey no hue matching will be done.
Hue Threshold: Used to control how close each pixels hue value needs to be to the selected Key Color to be treated as within the key.
Hue Softness: Used to soften the key in the hue channel.
Sat. Threshold: Used to control how close each pixels saturation value needs to be to the selected Key Color to be treated as within the key.
Sat. Softness: Used to soften the key in the saturation channel.
Lightness Threshold: Used to control how close each pixels lightness value needs to be to the selected Key Color to be treated as within the key.
Lightness Softness: Used to soften the key in the lightness channel.
Blur Key: Used to apply a blur to the key.
- Note: Use the Blur Key function with caution – it adds about 50 percent to the render time.
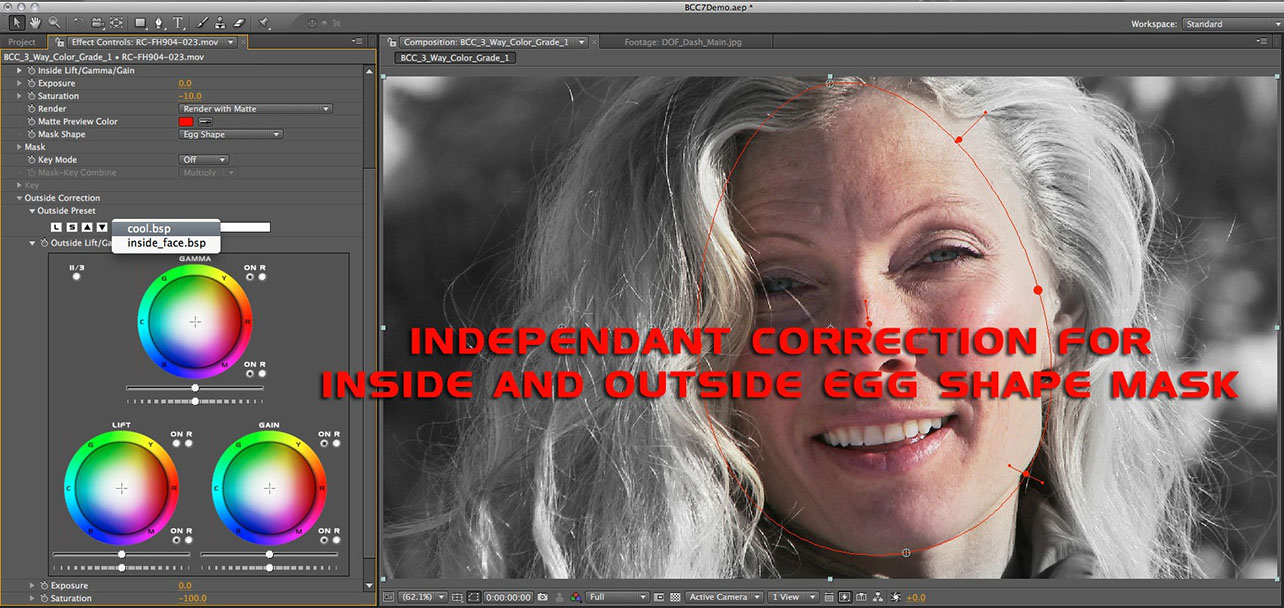
Outside Correction Group
This group contains a second set of color correction controls which are identical to the Inside Lift/Gamma/Gain and Exposure / Saturation functions at the top of the filter. This group of controls only effects regions that are outside of the key and / or mask and is disabled unless a live key or mask is present and seen by the filter. The parameters in this group are explained in the Left/Gamma/Gain group at the top of this document.
- Note: Presets can be shared between the inside and the outside color correction groups.
 Independent Inside vs Outside Correction
Independent Inside vs Outside Correction
Mix with Original: Mixes back the original image with the filtered result as in other BCC filters.
Motion Tracker
The BCC Motion Tracker allows you to track the motion of an object, then use the motion path to drive other geometric properties of the effect without the need for keyframing.
For more information on the Motion Tracker, Click Here.
Apply has three choices.
- Off: ignores the tracker data
- Mask Points: applies each tracker to the corresponding mask points
- Host Mask Offset: applies data from Tracker 1 to the host mask.
Lock Tracker 1 and 2 lock each tracker. If you have successfully tracked one point, and are still working on the other, you can lock the completed tracker to save time and avoid changing its data.
Each tracker has a group for controls that can be set independently for the trackers. You would normally set tracker 1 to the point at the start of your clip where you want Point 1 of the mask to be, and tracker 2 where you want Point 2. You would then track and set Apply to Mask Points
There will be times when the points that you are able to track do not correspond to the end points of the desired mask. There are two ways that you can deal with this. You can attempt to adjust the mask controls (e.g. Feather, Feather Bias, and Scale) to find settings that produce the desired result, or you can edit the Offset X and Offset Y controls for each point to offset the Mask Points from the tracked result. These offset controls can be animated if needed.