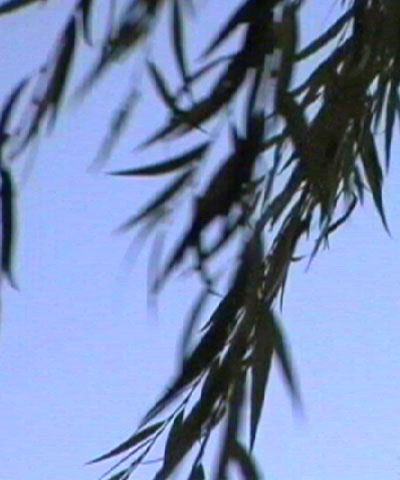
 |  |  |
| Source image | Source layer | Filtered image |
Overview
The Time Displacement filter is a displacement map that operates in time instead of in space. Pixels are displaced by mixing pixels from the source at the current frame with source pixels from previous or future frames. Basic frame blending is used to compute intermediate pixels and to produce anti-aliased result.
- Warning:You can apply the Time Displacement filter directly to the clip that you want to filter; however, the duration of the effect is then limited to the duration of the filtered clip. To create an effect that is longer than the duration of the source media, follow the steps described in the BCC Velocity Remap filter.
Function
Presets and Common Controls
BCC filters come with a library of factory installed presets plus the ability to create your own custom presets and preview them with the BCC FX Browser™.
BCC filters also include common controls that configure global effect preferences and other host-specific effect settings.
For more information about working with presets and other common controls, Click Here.
The Map Layer menu determines which layer in the timeline is used to create the distortions in the filtered image.
- Note: If the Map Layer is partly transparent, the displacement amount scales by its alpha values. Pixels whose map alpha is 0 are not displaced.
Map Parameter Group
The Map parameters control the appearance of the displacement map used to distort the source image.
- Note: The parameters in this section are identical to the corresponding controls in the Displacement Map filter. See the BCC Displacement Map filter for more information – Click Here.
The View Map checkbox allows you to view the Source Layer as you make adjustments to it. Deselect this option before rendering.
The Displacement Channel menu sets the channel in the Source Layer used to compute displacement. The choices are Red, Green, Blue, Luma, White, Gray, and Black. White treats all of the pixels as if they were white (i. e. fully displaces each pixel Displacement Amount value). Gray treats all of the pixels as if they were 50% gray (resulting in no displacement). Black treats all of the pixels as if they were black, thereby displacing all pixels to the negative of the Displacement Amount value.
Displacement Amount sets the number of frames between the most forward-displaced pixel and the most backward-displaced. For example, if Displacement Amount is 2 and Map Reference Level is 127.5, pixels whose value in the selected Displacement Channel is 255 are displaced forward 1 frame, and those whose value is 0 are displaced backward 1 frame.
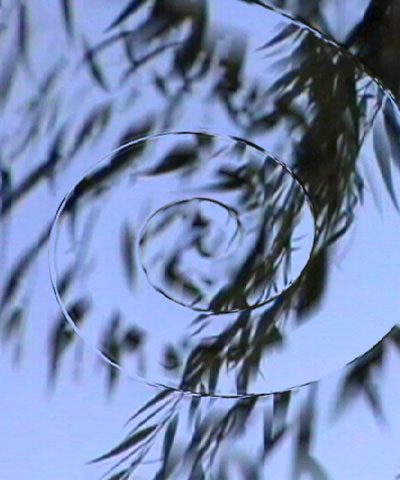 |  |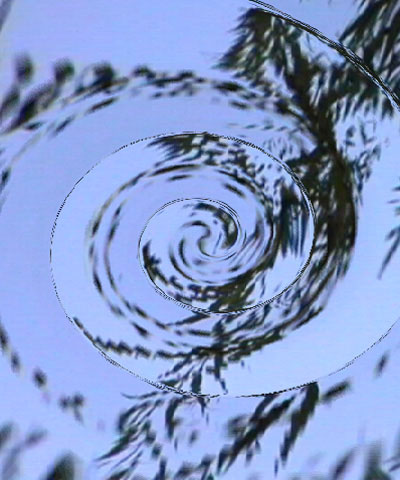  |
| Displacement Amount=5 | Displacement Amount=12 | Displacement Amount=20 |
Map Reference Level determines the channel value for which pixels are not displaced. For example, if Map Reference Level is 0, pixels whose values in the selected Displacement Channel are 0 are not displaced. Pixels whose value is 255 are displaced 2 frames forward. If Map Reference Level is 255, pixels whose value is 0 are displaced backwards 2 frames, and pixels whose value is 255 are not displaced.
Select the Frame Blending checkbox to enable frame blending. It is recommended that you leave this option selected, as Frame Blending prevents an aliased appearance in the render.
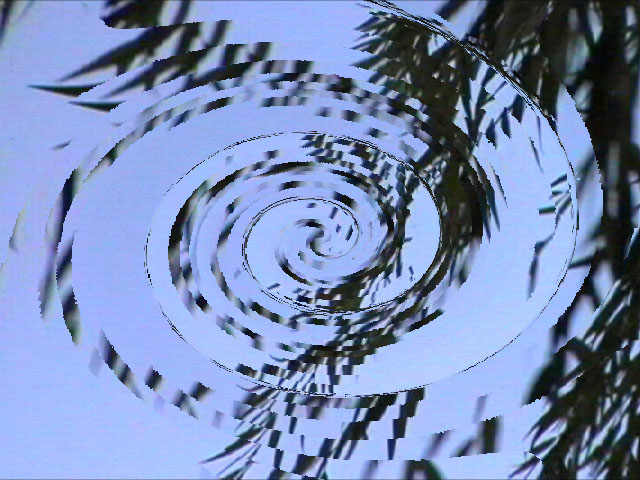 |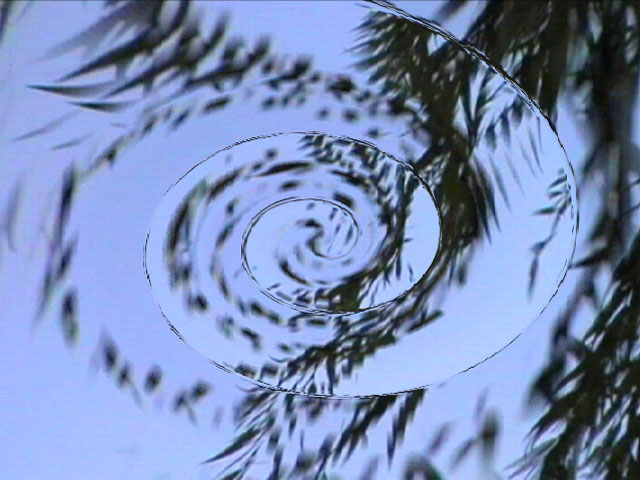  |
| Frame Blending off | Frame Blending on |
If the Deinterlace checkbox is selected, the program creates an in-between frame to use for the field opposite to the one being rendered, and use the new frames in the displacement render. This produces a smoother render, but it can be somewhat softer because the in- between fields are averaged to make a frame. The filter renders more slowly when Deinterlace is selected. This option is only used when the effect is field rendered; you cannot see the effect of Deinterlace in a preview.
End Behavior determines the behavior of the displacement map when the frame being rendered is the close to the first or last frame in the source media and the previous or future frame does not exist. For example, at the default settings in frame 0 the filter tries to mix the current frame with a previous frame (frame –1) which does not exist.
- Squeeze Map in Time uses the specified Displacement Amount where possible and squeezes the displacement map so that all pixels are displaced.
- Expand Map in Time expands the map in the direction which has enough pixels (in the example above, this would be in the future frames direction) to keep the distance in time between the maximum and minimum displacement equal to the Displacement Amount.
- Clip Map does not alter the map. The filter substitutes the closest existing frame for every frame that does not exist. This choice produces a render in which the displacement does not start for some pixels until after the start of the effect.
The Map Behavior setting determines how the map is applied when the source image is a different size than the image in the Source Layer. If your map is the same size as the image to which you are applying the filter, the Map Behavior settings all produce the same result.
- Center Map centers the map on the source and does not displace the source image outside the boundaries of the centered Source Layer.
- Stretch Map to Fit resizes the Source Layer to the size of the source.
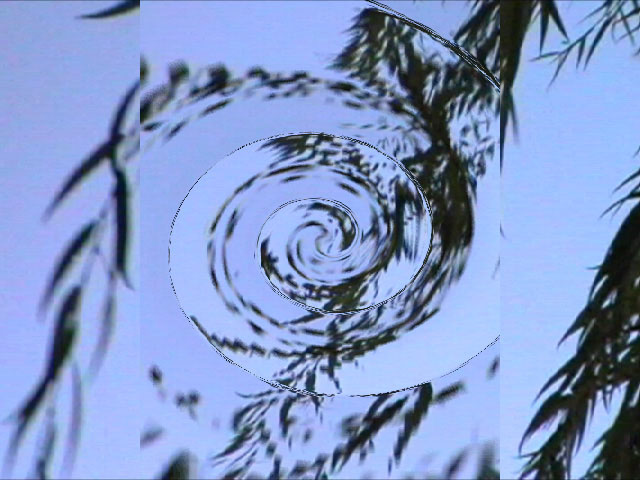 |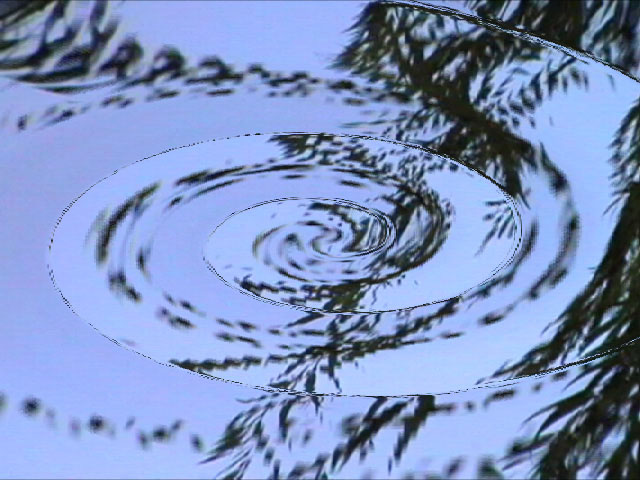  |
| Map Behavior=Center Map | Map Behavior=Stretch Map to Fit |
PixelChooser
The BCC PixelChooser provides simple, built-in masking of the effect result. The PixelChooser is generally used to select a portion of the image and restrict an effect to just the selected area while maintaining the original image content in unselected regions. The selection can be based on geometric shapes or on the image’s luma/color properties.
For more information on the PixelChooser, Click Here.








