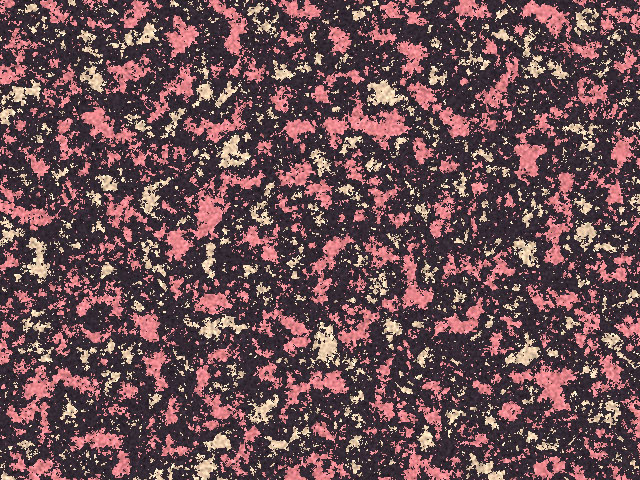
Overview
Granite simulates the appearance of granite or another type of mottled stone.
Function
Presets and Common Controls
BCC filters come with a library of factory installed presets plus the ability to create your own custom presets and preview them with the BCC FX Browser™.
BCC filters also include common controls that configure global effect preferences and other host-specific effect settings.
For more information about working with presets and other common controls, Click Here.
Offset XY controls the appearance of the granite pattern at a given point by moving through the procedural noise from which the effect is generated.
Scale X and Scale Y determine the scale of the pattern along the X and Y axis respectively. Select Lock to Scale X to keep these values in proportion, or deselect this option to adjust Scale X and Y independently.
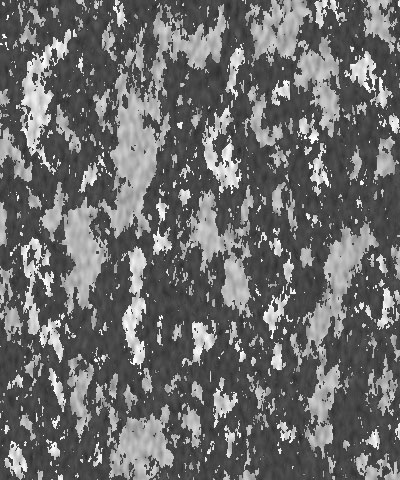 |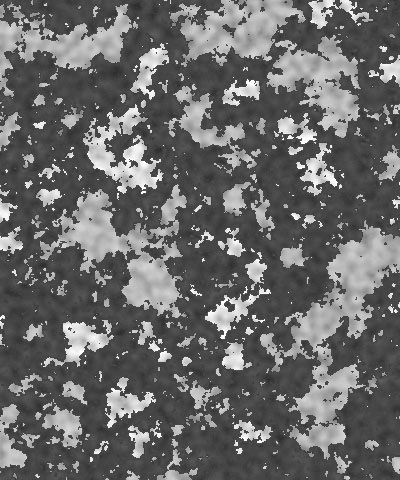  |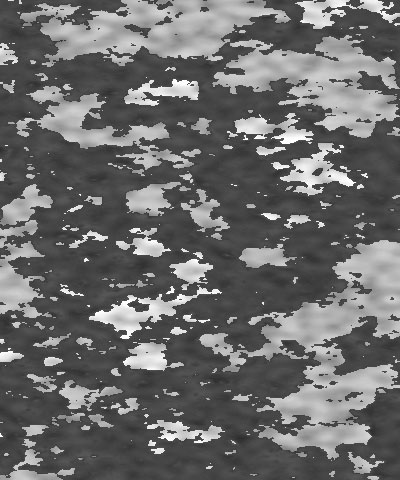  |
| Scale X=50 | Scale X=100 | Scale X=200 |
Rotation spins the granite pattern around the Z axis.
The Color 1 and Color 2 controls set the two colors that make up the marble pattern.
The Background Color controls set the background color in the marble pattern.
Color 1 Alpha, Color 2 Alpha and Background Alpha set the alpha value for the corresponding color.
The Color 1 Boundary and Color 2 Boundary settings adjust the relative sizes of the patches of the colors. Color 1 Boundary controls the area covered by Color 1 and 2. When Color 1 Boundary is at 0, the Color 1 display covers its maximum area. As Color 1 Boundary increases, Color 2 intrudes into Color 1, reducing the size of the Color 1 patches and increasing the size of the Color 2 patches. Color 2 Boundary controls the area covered by Color 2 and 3. As Color 2 Boundary increases, more of the Background Color patches intrude into the Color 2 patches. Adjust the Boundary settings to balance the pattern to get the look you want.
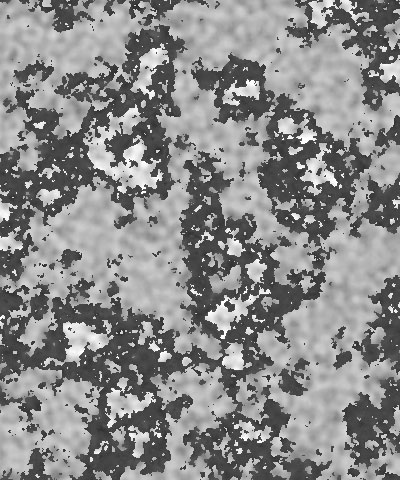 |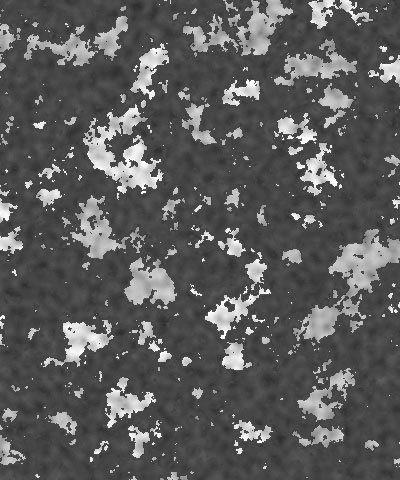  | 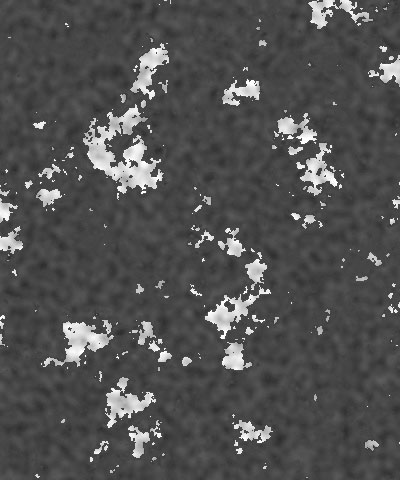 |
| Color 1 Boundary=0.0 | Color 1 Boundary=0.5 | Color 1 boundary=1.0 |
Border Blend softens the borders of the color patches. Higher values produce softer borders.
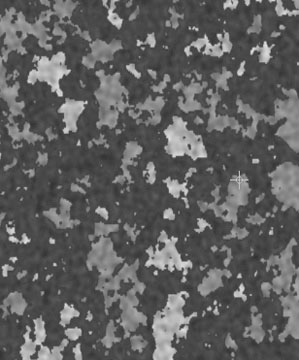 |  | 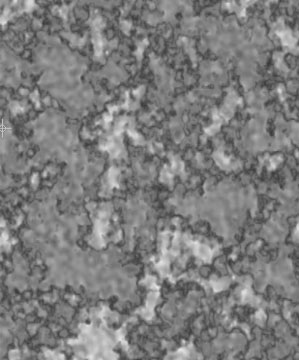 |
| Border Blend=0.0 | Border Blend=0.25 | Border Blend=0.5 |
Mutation controls the appearance of the granite pattern at a given point by moving through the procedural noise from which the effect is generated along the Z axis.
Cellularity reduces the complexity of the color patches in the texture, smoothing their edges and creating simpler shapes.
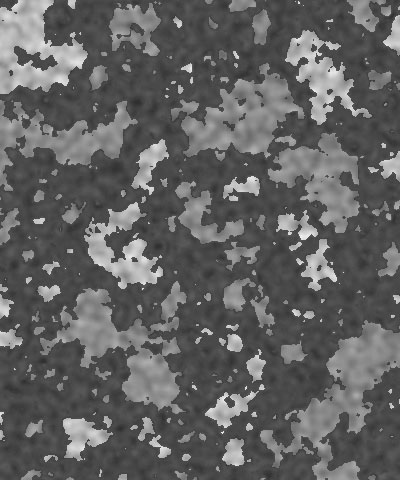 | 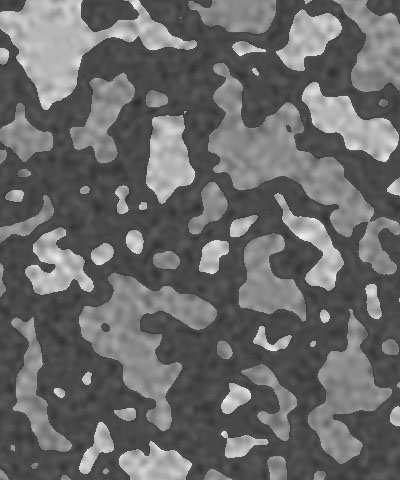 | 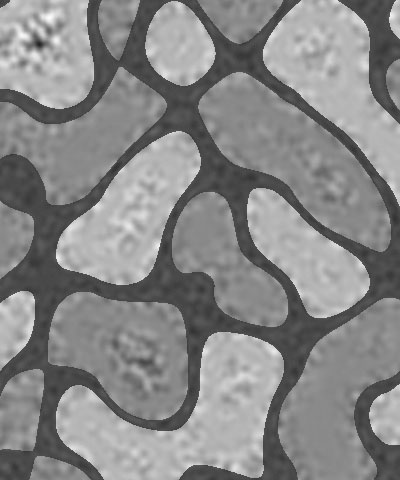 |
| Cellularity=0 | Cellularity=50 | Cellularity=100 |
Noise Overlay adjusts the intensity of the mottled noise texture which is overlaid on the color pattern. Decreasing this value decreases the intensity of the noise.
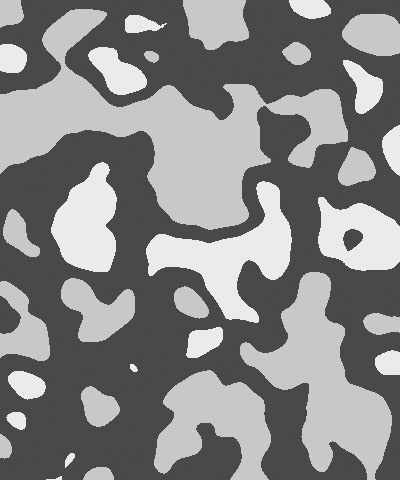 | 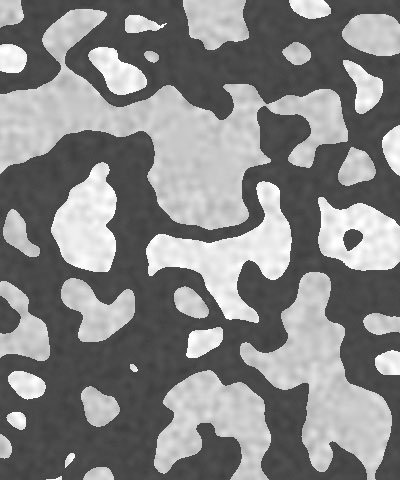 | 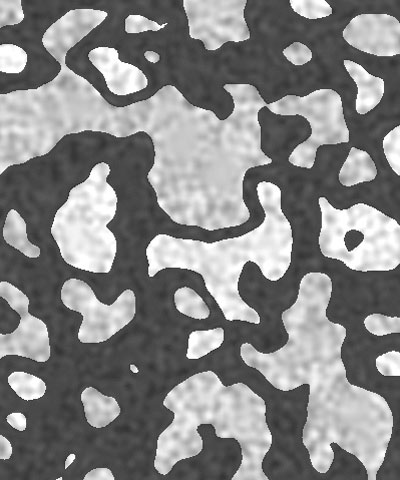 |
| Noise Overlay=0 | Noise Overlay=50 | Noise Overlay=100 |
Coarseness controls the number of distinct color patches that appear in the granite pattern. Higher values create a greater number of smaller patches, while lower values create a fewer patches that are larger in size.
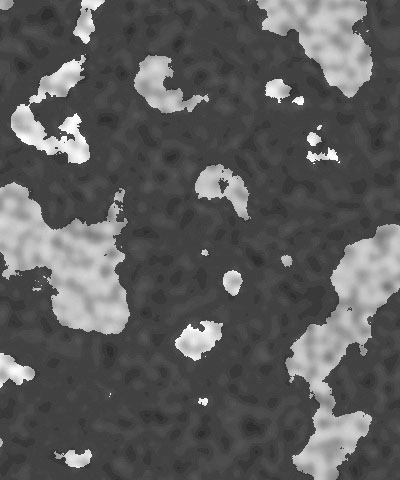 |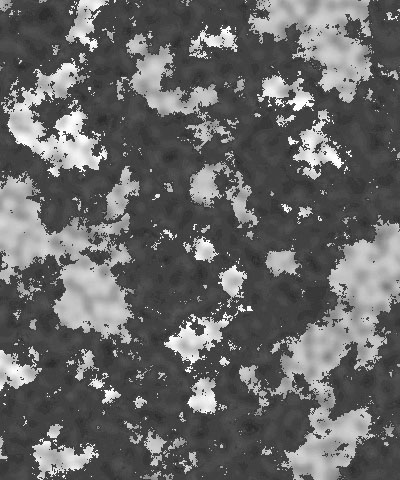  | 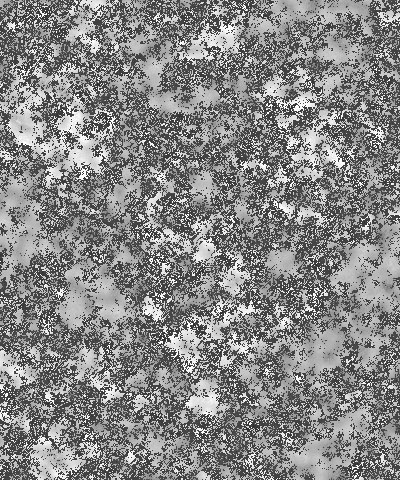 |
| Coarseness=10 | Coarseness=60 | Coarseness=100 |
Detail determines how jagged the boundaries between the three colors in the pattern are. Low values produce smooth curvilinear boundaries. High values produce rougher, more intricate boundaries.
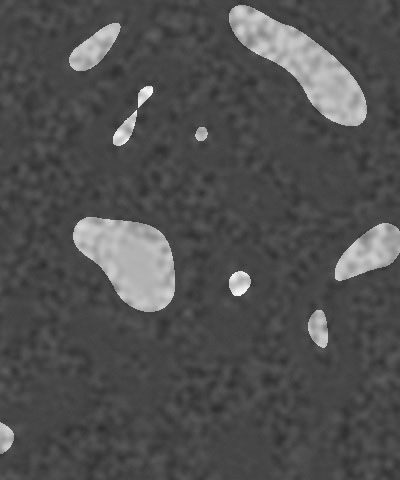 |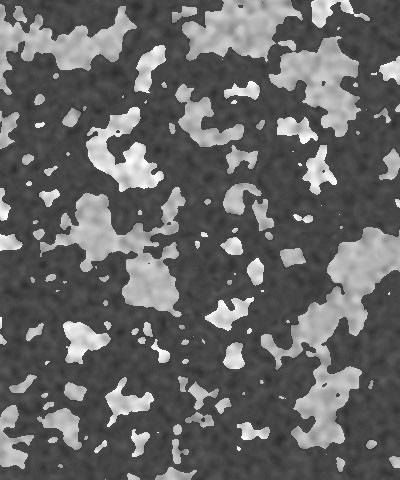  |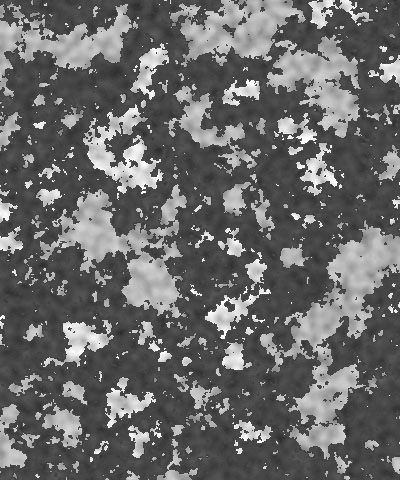  |
| Detail=10 | Detail=30 | Detail=50 |
Select the Source Alpha checkbox to use the source alpha channel as a mask for the filter, so the texture appears only in the opaque regions of the source. If this option is deselected, the source image’s alpha channel is ignored.
Opacity adjusts the opacity of the simulated texture.
The Apply Mode menu controls how the texture is composited over the source image. For descriptions of all the Apply Modes, Click Here.
Apply Mix controls the mix of the specified Apply Mode with the Normal apply mode. If the Apply Mode is Normal, Apply Mix has no affect. If Apply Mix is 0, Apply Mode has no affect. Increase Apply Mix to blend the Apply Mode setting with the Normal apply mode.
3D Bump Mapping Parameter Group
3D Bump Mapping is used to create the appearance of three-dimensional detail on a surface.
Select the Use Bump Map checkbox to turn on the Bump map. If this checkbox is not selected, the other parameters have no affect.
Light XY positions the light source in space by moving the light parallel to the image plane along the X and Y axes.
Light Z positions the depth of the light source relative to the image plane. A value of 100 places the light one source width above the image plane. Light Z can be negative, which places the light behind the image plane. If Light Z is negative, the light is seen only if the object is rotated or displaced so that all or part of it is behind the light source (that is, the light source always points in toward the object, never out at the viewer).
Light Intensity controls the intensity of the light.
Light Color controls the color of the light.
White in Specular increases the amount of white in the specular light. Increasing this value can create a more metallic surface effect. This parameter is only useful when Specular Intensity has a value greater than 0.
Ambient Intensity adjusts the total amount of diffuse light on the image. The default setting of 100 does not add or subtract ambient light from the source image. Decreasing this setting makes the image darker before the other lights are applied. Ambient light illuminates or darkens the image evenly, and is unaffected by any other lighting parameters.
Diffuse Intensity determines the amount of non-directional diffuse light applied to the object. Increasing Diffuse Intensity brightens the object uniformly.
Specular Intensity simulates lighting a glossy surface from a point source, creating a small spot of intense light whose falloff can vary. Increasing this value adds reflected light to the surface.
Shininess controls the rate at which the Specular light falls off from the center of the lit region. A higher Shininess value creates a more concentrated highlight, simulating a shiny, highly reflective surface. A lower Shininess value spreads light more evenly throughout the lit region, simulating a rougher, less reflective surface.
Bump Height determines the height of the bump map used to create the texture of the bricks.
Bump Smoothness adjusts the amount of blur applied to the bump map. Higher values produce more blur, which tends to reduce the amount of detail and noise in the filtered image.